134 Degrees F To K
timefordiamonds
Sep 23, 2025 · 6 min read
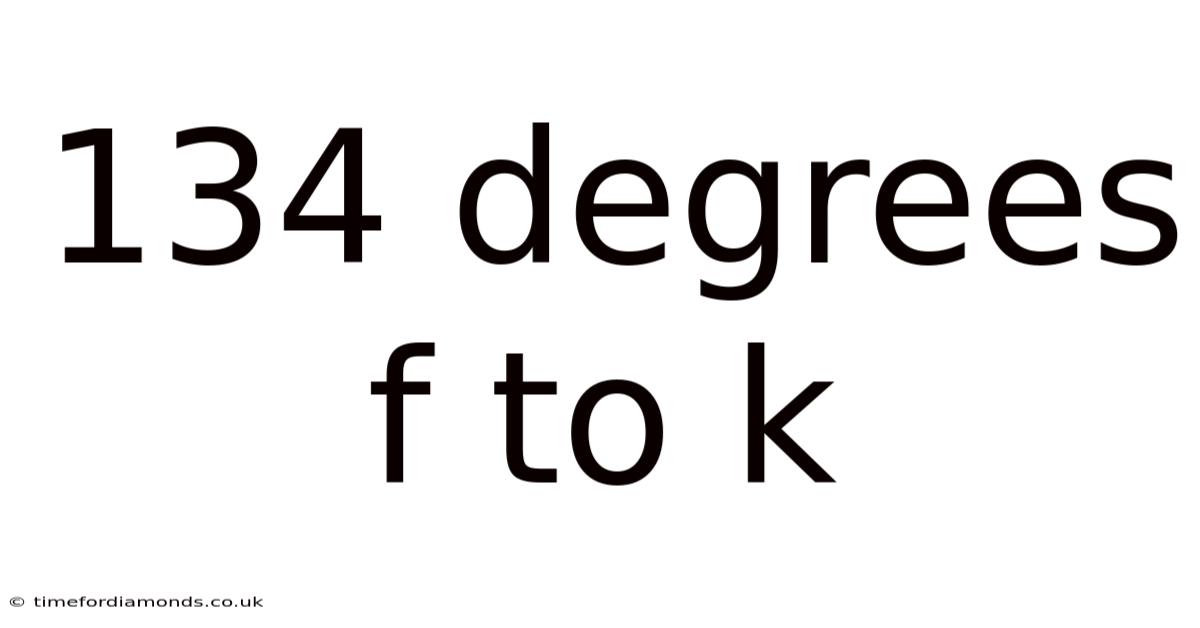
Table of Contents
Converting 134 Degrees Fahrenheit to Kelvin: A Comprehensive Guide
This article provides a comprehensive guide on converting 134 degrees Fahrenheit (°F) to Kelvin (K), explaining the process, the underlying scientific principles, and the practical applications of temperature conversions. Understanding temperature scales and their conversions is crucial in various fields, from cooking and meteorology to engineering and scientific research. This guide will not only show you how to convert 134°F to Kelvin but also equip you with the knowledge to perform similar conversions independently.
Understanding Temperature Scales
Before diving into the conversion, let's briefly review the three most common temperature scales: Celsius (°C), Fahrenheit (°F), and Kelvin (K).
-
Celsius (°C): Based on the freezing and boiling points of water at standard atmospheric pressure, 0°C is the freezing point and 100°C is the boiling point. Celsius is widely used globally and is the standard unit in the International System of Units (SI).
-
Fahrenheit (°F): Uses different fixed points, where the freezing point of water is 32°F and the boiling point is 212°F. It's primarily used in the United States.
-
Kelvin (K): An absolute temperature scale, meaning it starts at absolute zero – the theoretical point where all molecular motion ceases. 0 K is absolute zero, approximately -273.15°C or -459.67°F. Kelvin is used extensively in scientific calculations, particularly in thermodynamics and physics. Note that Kelvin doesn't use the degree symbol (°).
The Conversion Process: 134°F to Kelvin
The conversion from Fahrenheit to Kelvin involves two steps: first, converting Fahrenheit to Celsius, and then converting Celsius to Kelvin.
Step 1: Fahrenheit to Celsius
The formula for converting Fahrenheit to Celsius is:
°C = (°F - 32) × 5/9
Substituting 134°F into the formula:
°C = (134 - 32) × 5/9 = 102 × 5/9 ≈ 56.67°C
Step 2: Celsius to Kelvin
The formula for converting Celsius to Kelvin is:
K = °C + 273.15
Substituting 56.67°C into the formula:
K = 56.67 + 273.15 = 329.82 K
Therefore, 134°F is approximately equal to 329.82 Kelvin.
A Deeper Dive into the Scientific Principles
The conversion formulas are derived from the relationships between the fixed points of the different scales. The ratio 5/9 reflects the different magnitudes between a degree Celsius and a degree Fahrenheit. Adding 273.15 in the Celsius-to-Kelvin conversion accounts for the difference in the zero points of the two scales. The Kelvin scale is based on absolute zero, a fundamental concept in thermodynamics.
-
Absolute Zero: This is a theoretical temperature where all molecular motion stops. At this point, a substance possesses zero thermal energy. While it's impossible to reach absolute zero in practice, scientists continually approach it through techniques like laser cooling and magnetic trapping. The concept of absolute zero is critical for understanding various physical phenomena, including the behavior of gases and the limitations of energy extraction.
-
Thermodynamic Temperature: The Kelvin scale is a thermodynamic temperature scale, meaning it's independent of the properties of any specific substance. This contrasts with empirical scales like Celsius and Fahrenheit, which rely on the properties of water. The thermodynamic nature of Kelvin makes it the preferred scale in scientific research because it's more fundamental and robust.
-
Ideal Gas Law: The Kelvin scale plays a vital role in the ideal gas law (PV = nRT), where temperature must be expressed in Kelvin for accurate calculations. This law describes the relationship between pressure (P), volume (V), number of moles (n), and temperature (T) of an ideal gas. The constant R is the ideal gas constant. The accuracy of this law improves significantly at higher temperatures closer to ideal gas behaviour. Deviations from ideality become more pronounced at lower temperatures.
Practical Applications of Temperature Conversions
Understanding temperature conversions is essential in various fields:
-
Engineering: Engineers use these conversions extensively in designing systems that operate under various temperature conditions. For example, designing a heat exchanger requires accurate temperature conversions to ensure optimal performance and prevent damage due to overheating or freezing. Calculations involving thermal expansion, heat transfer, and fluid dynamics all require consistent use of the Kelvin scale for accuracy.
-
Meteorology: Weather reports might be given in Fahrenheit in some regions, but scientists use Celsius and Kelvin to analyze weather patterns and model climate change. Understanding the conversions is crucial for interpreting weather data from different sources and making accurate predictions.
-
Cooking: While recipes might use Fahrenheit, understanding the relationship between Fahrenheit and Celsius is important for accurate baking and cooking, particularly when working with international recipes.
-
Medicine: Body temperature is often measured in both Fahrenheit and Celsius. Understanding the conversion is crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
-
Material Science: Many material properties, like the melting point and boiling point, are often expressed in Celsius or Kelvin. Conversions are necessary when comparing materials with different reported temperature scales.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Why is Kelvin used in scientific calculations? Kelvin is an absolute temperature scale, meaning it starts at absolute zero, providing a more fundamental and consistent basis for scientific calculations. Many physical laws and equations are based on the Kelvin scale, making it essential for accurate results.
-
Can I convert directly from Fahrenheit to Kelvin without going through Celsius? Yes, you can. The combined formula is: K = (°F + 459.67) × 5/9. This formula directly accounts for the difference in zero points and scaling between the two scales.
-
What is the significance of absolute zero? Absolute zero is the theoretical point where all molecular motion stops, possessing zero thermal energy. It represents the lowest possible temperature, a fundamental concept in thermodynamics. While unreachable in practice, it serves as a crucial reference point in many scientific calculations.
-
Are there other temperature scales besides Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Kelvin? Yes, there are other scales, though less commonly used. For example, the Rankine scale is an absolute temperature scale based on Fahrenheit. Each scale has its specific applications and contexts.
Conclusion
Converting 134°F to Kelvin, which results in approximately 329.82 K, is a straightforward process involving two steps: converting Fahrenheit to Celsius and then Celsius to Kelvin. Understanding these conversions is vital for anyone working with temperatures in various scientific, engineering, and everyday applications. This article not only provides the practical method but also delves into the underlying scientific principles, highlighting the importance of the Kelvin scale in thermodynamic calculations and the significance of absolute zero. By grasping these concepts, you'll develop a deeper understanding of temperature and its crucial role in various fields. Remember that accuracy in temperature measurement and conversion is often critical for successful outcomes in many different endeavors.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
45 Degrees C To Fahrenheit
Sep 23, 2025
-
140 Degrees F In C
Sep 23, 2025
-
How Many Grams In 1000mg
Sep 23, 2025
-
145 Pounds Converted To Kg
Sep 23, 2025
-
1 M How Many Mm
Sep 23, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 134 Degrees F To K . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.