Lbf Ft To Kg M
timefordiamonds
Sep 19, 2025 · 7 min read
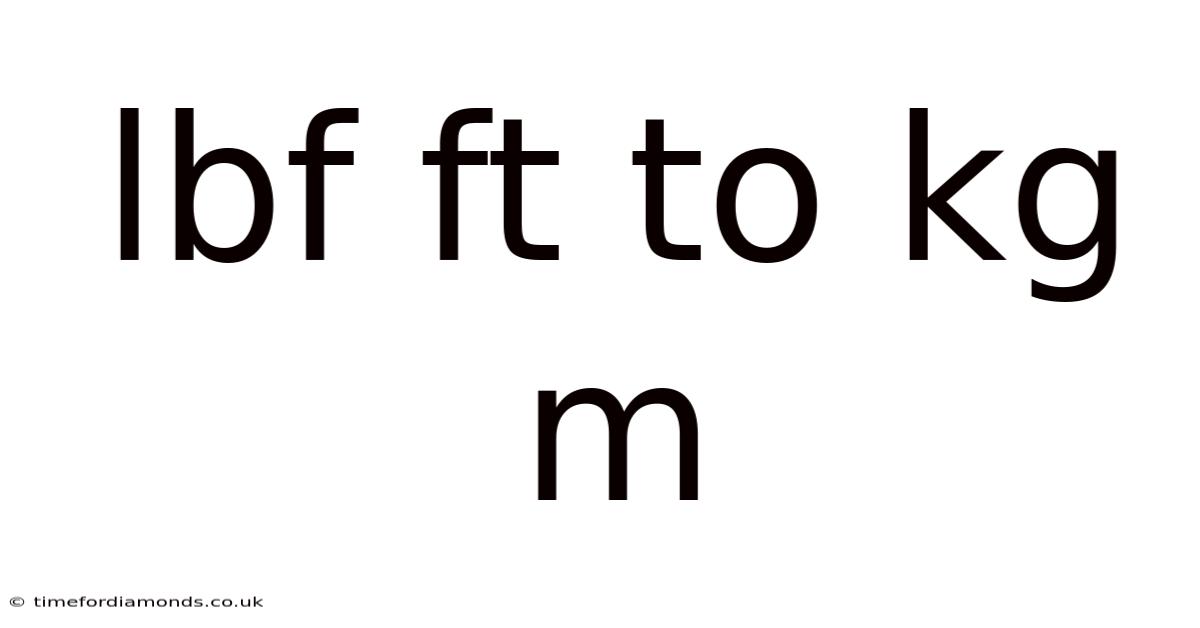
Table of Contents
Converting Lbf Ft to Kg m: A Comprehensive Guide for Understanding Units and Conversions
Understanding units and their conversions is crucial in various fields, from engineering and physics to everyday life. This comprehensive guide delves into the conversion between lbf ft (pound-force feet) and kg m (kilogram meters), two common units used to express energy or work. We'll explore the underlying principles, provide a step-by-step conversion process, and address frequently asked questions to ensure a thorough understanding of this important conversion.
Introduction
The units lbf ft and kg m both represent energy or work, but they are based on different systems of units. Lbf ft is part of the imperial or US customary system, while kg m belongs to the metric or International System of Units (SI). The conversion between these two involves understanding the base units within each system – pounds-force (lbf), feet (ft), kilograms (kg), and meters (m) – and their relationships to each other. This conversion is especially relevant in situations requiring interoperability between systems, such as international collaborations on engineering projects or comparing data from different sources. This article will empower you with the knowledge to confidently perform these conversions.
Understanding the Units
Before we dive into the conversion process, let's clarify the meaning of each unit involved:
-
Pound-force (lbf): This is a unit of force. One pound-force is the force required to accelerate a mass of one pound at a rate of 32.174 ft/s² (the standard acceleration due to gravity on Earth). It's important to distinguish this from the pound (lb), a unit of mass.
-
Foot (ft): This is a unit of length in the imperial system, approximately 0.3048 meters.
-
Kilogram (kg): This is the SI unit of mass. It's a fundamental unit in the SI system.
-
Meter (m): This is the SI unit of length. It's also a fundamental unit in the SI system.
The Conversion Process: From Lbf Ft to Kg m
The conversion from lbf ft to kg m is not a simple one-to-one ratio. It requires considering the conversion factors for both force and length. Here's a step-by-step approach:
-
Convert pound-force (lbf) to Newtons (N): The Newton (N) is the SI unit of force. The conversion factor is:
1 lbf ≈ 4.44822 N
-
Convert feet (ft) to meters (m): The conversion factor is:
1 ft ≈ 0.3048 m
-
Calculate the energy in Joules (J): Work or energy is calculated as force multiplied by distance. Since 1 Joule (J) is equal to 1 Newton-meter (N⋅m), we can calculate the energy in Joules:
Energy (J) = Force (N) × Distance (m)
-
Convert Joules (J) to kilogram-meters (kg m): While Joules are the standard SI unit for energy, it's sometimes expressed as kg m, representing the product of mass and distance. However, it's important to note that this representation is less precise and doesn't directly relate to the standard definition of energy (Joules) which is a result of force and displacement. We need a different method for a more direct kg m equivalent.
A More Precise Approach: Focusing on Potential Energy
The lbf ft unit often represents potential energy, particularly in mechanical engineering contexts. Potential energy is the energy stored in an object due to its position or configuration. If we assume the lbf ft value represents potential energy, the conversion becomes more straightforward and accurate.
Potential Energy (PE) = mgh
Where:
- m = mass (kg)
- g = acceleration due to gravity (approximately 9.81 m/s²)
- h = height (m)
Following these steps gives us a far better representation. We'll use an example to illustrate:
Example:
Let's say we have a value of 100 lbf ft. Let's convert this to an equivalent in kg m.
-
Convert lbf to N: 100 lbf * 4.44822 N/lbf ≈ 444.822 N
-
Convert ft to m: Let's assume this 100 lbf ft represents potential energy, implying a force applied across a vertical distance (height). If we assume the height was 1 ft, then the calculation is:
1 ft * 0.3048 m/ft ≈ 0.3048 m
-
Calculate the work/potential energy in Joules: 444.822 N * 0.3048 m ≈ 135.58 J
-
Analyzing for mass in kgm. If we assume this is potential energy (PE = mgh), we can solve for 'm' using g= 9.81 m/s² and h = 0.3048 m:
135.58 J = m * 9.81 m/s² * 0.3048 m
Solving for 'm': m ≈ 44.48 kg
Therefore, our 100 lbf ft of potential energy, with a height of 1 ft, could be approximately represented as 44.48 kg * 0.3048m. This highlights the importance of knowing the context (potential energy or work) for the most accurate conversion. The product of mass and distance on its own isn't a directly analogous representation to energy.
Explanation of the Scientific Principles
The conversion relies on fundamental principles of physics:
-
Newton's Second Law: This law (F=ma) connects force (F), mass (m), and acceleration (a). It's essential for understanding the relationship between lbf and N.
-
Work-Energy Theorem: This theorem states that the work done on an object is equal to the change in its kinetic energy. Work is calculated as force multiplied by distance, leading to the use of Joules (N⋅m) as the unit of energy.
-
Units Conversion: The conversion process hinges on the application of appropriate conversion factors between imperial and metric units. Accurate conversion factors are critical for obtaining reliable results.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
What if the lbf ft value doesn't represent potential energy? If the lbf ft value represents work done in a non-vertical direction, the conversion process remains similar in principle. You'd convert lbf to N and ft to m, and the result will be in Joules (J). However, you won't be able to directly convert to kg m since that representation is most commonly associated with potential energy. The Joules (J) are the most appropriate unit to use in such cases.
-
Why is there a difference in the results? The discrepancy arises from the fundamental differences between the systems of units. The imperial system is based on pound-force and feet, while the metric system is built upon the kilogram and meter. Each unit has a specific definition, resulting in different conversion factors. The context of potential energy or work is also essential for a meaningful interpretation of the result.
-
Are there online converters available? Yes, numerous online converters are available to perform this conversion. However, understanding the underlying principles is crucial to avoid misinterpretations and to properly apply the conversion in different contexts.
-
Is kg m equivalent to Joules? No, kg m is not directly equivalent to Joules. While both represent energy, kg m is not a standardized unit for energy. The most appropriate and universally accepted unit for energy is the Joule (J). A kg m representation arises from the equation for potential energy (PE = mgh), but applying this conversion requires knowing the context and the height (h).
Conclusion
Converting lbf ft to kg m requires a careful understanding of the underlying units and their relationships. The conversion isn't a simple multiplication but involves several steps, including converting force and length to their SI equivalents. The most accurate and meaningful conversion depends heavily on understanding whether the initial value represents potential energy or work performed in a general sense. The result should then be expressed using the standard unit of energy, which is the Joule (J). While approximations using kg m may sometimes be possible for potential energy, this needs careful handling and a clear understanding of the context. Remember, always prioritize clarity and precision when working with units to ensure the accuracy and reliability of your calculations. This comprehensive guide provides you with the knowledge and tools to perform these conversions confidently and accurately.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Long Is 3 Inches
Sep 20, 2025
-
What Is 120kg In Pounds
Sep 20, 2025
-
3 Pounds How Many Grams
Sep 20, 2025
-
38 Degrees C In F
Sep 20, 2025
-
30ml Is How Many Teaspoons
Sep 20, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Lbf Ft To Kg M . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.