97. 6 F To C
timefordiamonds
Sep 17, 2025 · 6 min read
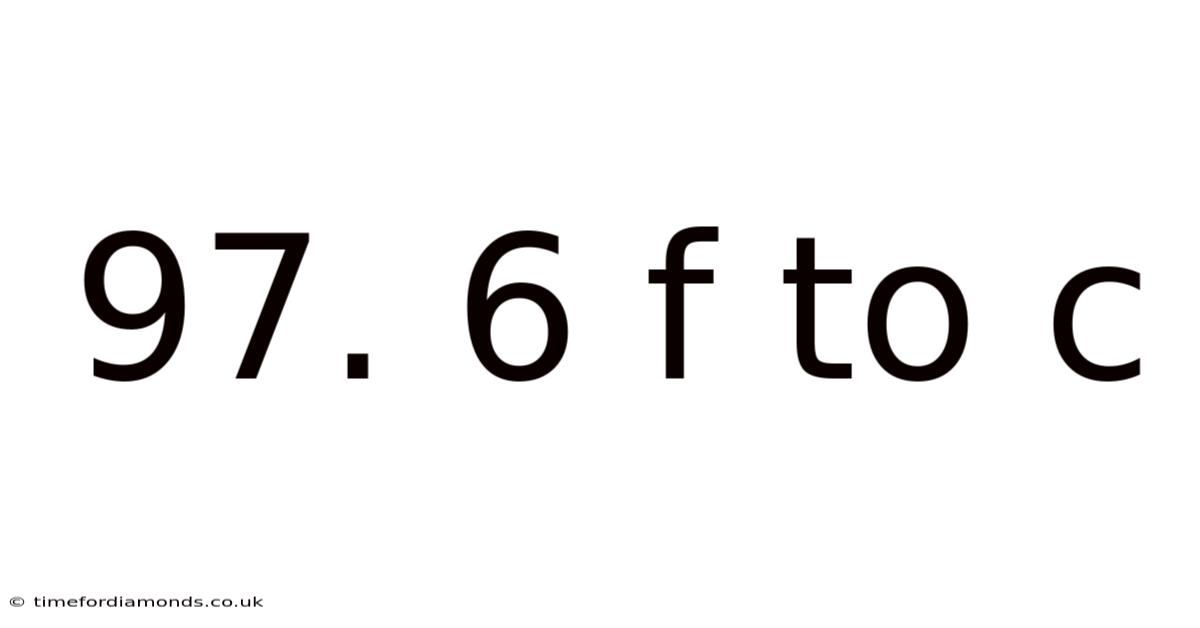
Table of Contents
Decoding 97.6°F to Celsius: A Comprehensive Guide to Temperature Conversion
Have you ever wondered how to convert Fahrenheit to Celsius? Understanding temperature conversions is crucial in various fields, from cooking and meteorology to engineering and medicine. This comprehensive guide will not only show you how to convert 97.6°F to Celsius but will also delve into the underlying principles, explore practical applications, and answer frequently asked questions. This will equip you with a thorough understanding of temperature scales and conversion methods.
Understanding Fahrenheit and Celsius
Before we jump into the conversion of 97.6°F, let's briefly understand the two temperature scales: Fahrenheit (°F) and Celsius (°C).
-
Fahrenheit (°F): This scale is primarily used in the United States and a few other countries. It's based on a scale where the freezing point of water is 32°F and the boiling point is 212°F.
-
Celsius (°C): This scale, also known as the centigrade scale, is the most widely used temperature scale globally. It's based on a scale where the freezing point of water is 0°C and the boiling point is 100°C.
The difference between the two scales lies in their reference points and the size of their degree units. A degree Celsius is larger than a degree Fahrenheit. This means a smaller change in Celsius represents a larger change in Fahrenheit.
Converting 97.6°F to Celsius: The Formula and Calculation
The standard formula for converting Fahrenheit to Celsius is:
°C = (°F - 32) × 5/9
Let's apply this formula to convert 97.6°F:
-
Subtract 32 from the Fahrenheit temperature: 97.6°F - 32°F = 65.6°F
-
Multiply the result by 5/9: 65.6°F × 5/9 = 36.44°C
Therefore, 97.6°F is equivalent to 36.44°C.
Practical Applications and Significance of 36.44°C
A temperature of 36.44°C (or 97.6°F) holds significance in various contexts:
-
Human Body Temperature: While the average human body temperature is often cited as 37°C (98.6°F), slight variations are normal. A temperature of 36.44°C falls within the range considered normal for many individuals, though it's slightly below average. Factors such as time of day, activity level, and individual variations can affect body temperature. It's crucial to consult a medical professional if you experience persistent deviations from your usual body temperature range.
-
Environmental Conditions: A temperature of 36.44°C represents a warm environment, comfortable for some but potentially uncomfortable or even dangerous for others depending on humidity levels and acclimatization. This temperature would likely be considered warm for many indoor environments, potentially requiring adjustments to climate control systems. In outdoor settings, this temperature could be pleasant in the evening but may become excessively hot during the day.
-
Scientific Experiments and Industrial Processes: In scientific research and industrial processes, precise temperature control is often vital. Converting between Fahrenheit and Celsius is essential to ensure accurate readings and maintain consistent conditions across different measurement systems.
-
Cooking and Baking: While many recipes might use Fahrenheit, understanding the Celsius equivalent is crucial, particularly when using international recipes or adjusting baking times. Accurate temperature control is key to successful cooking and baking.
Beyond the Calculation: A Deeper Dive into Temperature Scales
The conversion formula itself is based on the relationship between the freezing and boiling points of water in both Fahrenheit and Celsius. Let's explore this relationship further:
-
Freezing Point of Water: 0°C and 32°F
-
Boiling Point of Water: 100°C and 212°F
Notice that there is a 100°C difference between the freezing and boiling points of water on the Celsius scale and a 180°F difference on the Fahrenheit scale. The ratio between these differences is 100/180, which simplifies to 5/9. This ratio is the core of the conversion formula.
This highlights the fact that a single degree Celsius represents a larger temperature change than a single degree Fahrenheit. The 5/9 factor in the conversion formula accounts for this difference in the scale's size.
Other Temperature Scales: Kelvin and Rankine
While Celsius and Fahrenheit are the most common scales, it's worth mentioning two other scales: Kelvin (K) and Rankine (°R).
-
Kelvin (K): This is an absolute temperature scale, meaning it starts at absolute zero – the theoretical point where all molecular motion ceases. 0 K is equivalent to -273.15°C. Kelvin is widely used in scientific calculations and research, especially in fields like thermodynamics.
-
Rankine (°R): This is another absolute temperature scale, related to Fahrenheit in the same way Kelvin is related to Celsius. 0°R is equivalent to -459.67°F.
Converting between these scales requires additional formulas which are slightly more complex than the Fahrenheit-Celsius conversion.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Is 97.6°F a cause for concern?
A: A single reading of 97.6°F might not be cause for immediate concern, as individual body temperatures can vary. However, if you are experiencing other symptoms or if this temperature persists or changes significantly, it's crucial to consult a doctor.
Q: Can I use an online converter instead of the formula?
A: Yes, many online calculators are readily available for converting between Fahrenheit and Celsius. These tools can be helpful for quick conversions. However, understanding the underlying formula ensures that you can perform the conversion even without access to a calculator or the internet.
Q: What is the difference between a degree Celsius and a degree Fahrenheit?
A: A degree Celsius represents a larger temperature change than a degree Fahrenheit. The ratio is 5/9, meaning a 1°C change is equivalent to a 1.8°F change.
Q: Why are there different temperature scales?
A: Different scales developed historically due to variations in measurement systems and scientific understanding. While Celsius has become the global standard for most applications, Fahrenheit remains prevalent in some regions due to established practices.
Q: Are there any significant errors that can arise from improper conversion?
A: Yes, especially in scientific experiments, industrial processes, or medical settings, inaccurate conversions can lead to significant problems. Errors could lead to incorrect diagnoses, equipment malfunction, or flawed experimental results. Accuracy is paramount.
Conclusion
Converting 97.6°F to Celsius illustrates the importance of understanding temperature scales and their conversion. This guide not only provides a clear step-by-step process for the conversion itself (resulting in 36.44°C) but also offers a deeper understanding of the underlying principles and the significance of temperature in various contexts. Remembering the conversion formula and its derivation will empower you to confidently handle temperature conversions in numerous situations. Remember to always consult with professionals when dealing with medical or critical industrial applications. This knowledge will serve you well in both personal life and professional endeavors.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Conversion De Unidades De Peso
Sep 17, 2025
-
Cubic Inch To Cubic Mm
Sep 17, 2025
-
Cuantas Onzas Tiene Un Kilogramo
Sep 17, 2025
-
6 7 Pulgadas A Cm
Sep 17, 2025
-
23 Grad Celsius In Fahrenheit
Sep 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 97. 6 F To C . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.