500 Deg F To C
timefordiamonds
Sep 14, 2025 · 5 min read
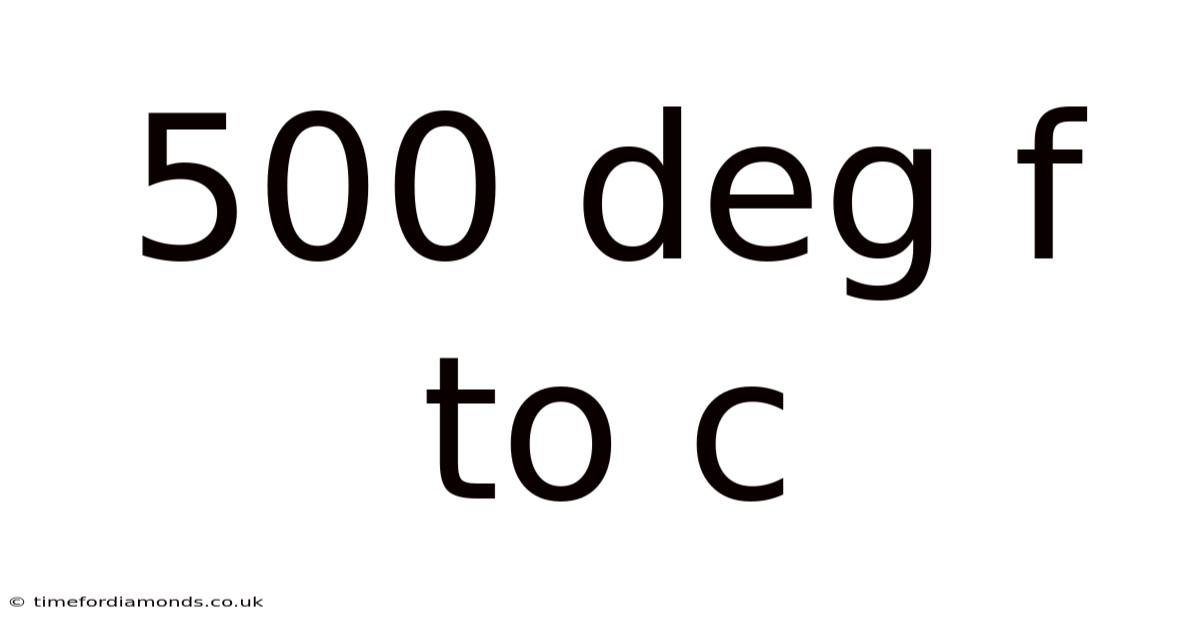
Table of Contents
500°F to °C: Understanding Temperature Conversions and Their Applications
Converting temperatures between Fahrenheit (°F) and Celsius (°C) is a common task in many fields, from cooking and everyday life to scientific research and engineering. Understanding this conversion is crucial for accurate measurements and effective communication across different systems. This comprehensive guide will not only show you how to convert 500°F to °C but will also delve into the underlying principles, provide practical examples, and explore the applications of this temperature range in various contexts.
Understanding Fahrenheit and Celsius Scales
Before diving into the conversion, let's briefly revisit the Fahrenheit and Celsius scales. Both are used to measure temperature, but they differ in their reference points.
-
Fahrenheit (°F): This scale, developed by Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit, uses the freezing point of water as 32°F and the boiling point of water as 212°F at standard atmospheric pressure.
-
Celsius (°C): Also known as the centigrade scale, Celsius uses the freezing point of water as 0°C and the boiling point of water as 100°C at standard atmospheric pressure. This scale is widely used in most of the world and is the preferred system in science.
Converting 500°F to °C
The formula to convert Fahrenheit to Celsius is:
°C = (°F - 32) × 5/9
Let's apply this formula to convert 500°F:
°C = (500 - 32) × 5/9 = 468 × 5/9 = 260°C
Therefore, 500°F is equal to 260°C.
Practical Applications of 260°C (500°F)
A temperature of 260°C (500°F) represents a significant heat level with diverse applications across various industries and everyday scenarios. Let's explore some of them:
1. Cooking and Baking:
While not a commonly used temperature for everyday baking, 260°C (500°F) finds its application in specific cooking techniques. High-temperature searing of meats, achieving a desirable crust on pizzas or breads in specialized ovens, and certain types of specialized candy-making might involve this temperature range. It’s crucial to understand that precise temperature control is essential at this level to prevent burning or uneven cooking.
2. Industrial Processes:
Many industrial processes operate at or around 260°C (500°F). This temperature range is prevalent in:
-
Metalworking: Heat treating of metals, such as annealing or hardening processes, often require temperatures within this range. The specific temperature depends on the type of metal and the desired properties.
-
Ceramics and Glass Manufacturing: Firing ceramics and shaping glass often involves temperatures around 500°F (260°C). This heat is crucial for vitrification and achieving the desired strength and properties in the final product.
-
Chemical Processes: Several chemical reactions and processes occur at high temperatures, some falling within the 260°C (500°F) range. Chemical engineers precisely control these temperatures to optimize reaction rates and yields.
3. Scientific Research:
In scientific research, especially in materials science and chemistry, precise temperature control is paramount. Experiments involving high-temperature reactions, material characterization at elevated temperatures, and thermal analysis often require maintaining and measuring temperatures around 260°C (500°F). Specialized equipment is employed to ensure accurate readings and consistent temperature control.
4. Other Applications:
-
HVAC Systems: Although less common, some industrial or specialized HVAC systems might operate at temperatures approaching this range, especially in high-heat industrial settings.
-
Automotive Components: Certain components of vehicles might endure temperatures in this range during operation, necessitating the use of heat-resistant materials.
Safety Precautions at High Temperatures
Working with temperatures as high as 260°C (500°F) necessitates stringent safety measures to prevent accidents and injuries. These include:
-
Proper Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): This includes heat-resistant gloves, eye protection, and clothing to protect against burns and thermal hazards.
-
Ventilation: Adequate ventilation is critical to prevent the buildup of harmful gases or fumes that may be generated at these temperatures.
-
Emergency Procedures: Having established emergency procedures and readily available firefighting equipment is essential in case of any incidents.
-
Equipment Maintenance: Regular maintenance and inspection of heating equipment are crucial to prevent malfunctions that could lead to accidents.
Understanding Temperature Scales Beyond Fahrenheit and Celsius:
While Fahrenheit and Celsius are the most commonly used scales, it's worth mentioning other important temperature scales:
-
Kelvin (K): This is the absolute temperature scale, where 0 K represents absolute zero – the theoretical lowest possible temperature. The Kelvin scale is extensively used in scientific research and engineering. The conversion from Celsius to Kelvin is straightforward: K = °C + 273.15. Therefore, 260°C is equal to 533.15 K.
-
Rankine (R): This absolute scale is used primarily in some engineering applications and is related to the Fahrenheit scale. The conversion from Fahrenheit to Rankine is R = °F + 459.67. Thus, 500°F equals 959.67 R.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Is it safe to touch something at 500°F (260°C)?
A: Absolutely not. 260°C (500°F) is extremely hot and will cause severe burns on contact. Always use appropriate safety measures and protective equipment when dealing with such high temperatures.
Q: What materials can withstand 500°F (260°C)?
A: Many materials can withstand 260°C (500°F), but their suitability depends on the specific application and duration of exposure. Examples include certain types of stainless steel, high-temperature alloys, ceramics, and some specialized polymers.
Q: How accurate is the conversion formula?
A: The conversion formula provided is highly accurate for most practical purposes. Minor discrepancies might arise due to variations in atmospheric pressure or other environmental factors, but these are generally negligible.
Q: Are there online calculators for temperature conversions?
A: Yes, numerous online calculators are readily available to perform conversions between different temperature scales, including Fahrenheit and Celsius. These tools can be helpful for quick conversions.
Conclusion:
Converting 500°F to 260°C is a simple yet crucial calculation with wide-ranging applications. Understanding the underlying principles of temperature scales and the various contexts in which this temperature range is utilized is essential for professionals and individuals across diverse fields. Always prioritize safety when dealing with high temperatures and remember the significance of precise measurements and appropriate safety precautions. This knowledge empowers you to navigate the world of temperature conversions confidently and safely, whether in the kitchen, the laboratory, or the industrial setting.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
73 Square Meters To Feet
Sep 14, 2025
-
How Many Ounces Is 45g
Sep 14, 2025
-
23 Degree Celsius To Fahrenheit
Sep 14, 2025
-
7 8 Oz To Grains
Sep 14, 2025
-
74 Grados Fahrenheit A Celsius
Sep 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 500 Deg F To C . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.