45 Deg C To F
timefordiamonds
Sep 12, 2025 · 5 min read
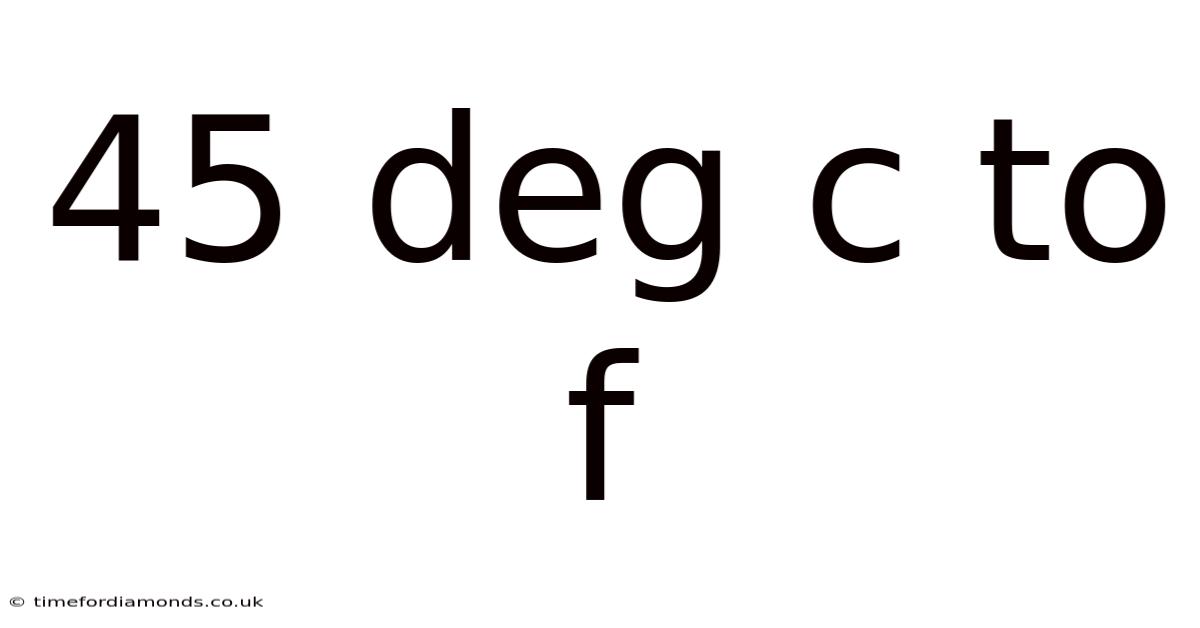
Table of Contents
45°C to °F: Understanding Celsius to Fahrenheit Conversion and its Applications
Converting temperatures between Celsius (°C) and Fahrenheit (°F) is a common task encountered in everyday life and various scientific and engineering applications. This comprehensive guide will not only show you how to convert 45°C to Fahrenheit but also delve into the underlying principles, provide multiple conversion methods, explore real-world applications, and answer frequently asked questions. Understanding temperature conversion is crucial for accurate measurements and informed decision-making across numerous fields.
Introduction: The Importance of Temperature Conversion
Temperature is a fundamental physical quantity that measures the degree of hotness or coldness of a substance. While Celsius is widely used globally, especially in scientific contexts, Fahrenheit remains prevalent in some countries, particularly the United States. The ability to seamlessly convert between these scales is essential for clear communication, accurate data analysis, and effective problem-solving in various situations, ranging from everyday cooking to complex industrial processes. This article will focus on the conversion of 45°C to °F, providing a clear and detailed explanation for readers of all levels of understanding.
Understanding the Celsius and Fahrenheit Scales
Before delving into the conversion, let's briefly understand the two scales:
-
Celsius (°C): Based on the freezing and boiling points of water at standard atmospheric pressure, set at 0°C and 100°C, respectively. This is also known as the centigrade scale.
-
Fahrenheit (°F): A scale where the freezing point of water is 32°F and the boiling point is 212°F. The difference between these points is divided into 180 degrees.
The difference in the scales stems from differing historical development and the choice of reference points. The key to conversion lies in understanding the relationship between these reference points and the linear relationship between the scales.
Methods for Converting 45°C to °F
There are several ways to convert 45°C to °F. Here are the most common methods:
1. Using the Conversion Formula:
The most straightforward method involves applying the standard conversion formula:
°F = (°C × 9/5) + 32
Substituting 45°C into the formula:
°F = (45 × 9/5) + 32 = 81 + 32 = 113°F
Therefore, 45°C is equal to 113°F.
2. Using a Conversion Table:
While not as flexible as the formula, pre-calculated conversion tables can provide a quick answer. These tables list corresponding Celsius and Fahrenheit values, allowing for direct lookup. However, for values not listed in the table, the formula remains necessary.
3. Using Online Converters:
Numerous online calculators and converters are readily available. These tools simplify the process, instantly providing the equivalent Fahrenheit value when you input the Celsius value. While convenient, understanding the underlying formula remains valuable for comprehension and problem-solving.
Real-World Applications of Celsius to Fahrenheit Conversion
The need to convert between Celsius and Fahrenheit arises in a wide range of contexts:
-
Meteorology: Weather reports often provide temperatures in both scales to cater to different audiences. Converting between the scales helps in understanding global weather patterns and comparing temperatures across different regions.
-
Cooking and Baking: Recipes might use either Celsius or Fahrenheit, depending on their origin. Accurate conversion is vital for achieving desired results in cooking and baking. Slight temperature variations can significantly impact the outcome.
-
Medicine: Body temperature is commonly measured in both Celsius and Fahrenheit. Conversion is important for international medical collaboration and understanding patient records from different regions.
-
Industrial Processes: Many industrial processes require precise temperature control. Accurate conversions are essential for ensuring consistency and optimal performance of machinery and equipment. Temperature monitoring and control systems often have the capability to display readings in both units.
-
Engineering: Engineering projects often involve calculations using different temperature scales. Converting temperatures ensures accurate calculations and design parameters, ensuring the structural integrity and functionality of engineered systems.
-
Science and Research: Scientific research frequently involves temperature measurements and data analysis. Conversion is critical for data comparison and interpretation across different studies and experimental setups.
Detailed Explanation of the Conversion Formula
The formula °F = (°C × 9/5) + 32 is derived from the relationship between the freezing and boiling points of water in both scales.
-
The ratio 9/5: This reflects the difference in the size of the degree intervals between the two scales. The 100-degree range in Celsius (0°C to 100°C) corresponds to a 180-degree range in Fahrenheit (32°F to 212°F). Therefore, 180/100 simplifies to 9/5. This factor scales the Celsius value to account for the difference in the degree interval sizes.
-
Adding 32: This accounts for the offset in the zero points of the two scales. The freezing point of water is 0°C but 32°F. This constant is added to align the Fahrenheit scale with the Celsius scale.
Understanding this formula’s derivation helps appreciate the mathematical relationship between the two temperature scales.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Why are there two different temperature scales? Historically, different scales emerged independently, reflecting the preferences and conventions of different scientific communities and regions.
-
Which scale is more accurate? Both scales are equally accurate; they simply use different reference points and degree intervals. The choice of scale often depends on convention and regional preference.
-
Are there other temperature scales besides Celsius and Fahrenheit? Yes, the Kelvin scale is widely used in scientific applications, particularly in thermodynamics. Kelvin is an absolute temperature scale, where 0 Kelvin represents absolute zero.
-
Can I convert negative Celsius temperatures to Fahrenheit? Yes, the formula works for both positive and negative temperatures. Remember that the resulting Fahrenheit temperature might also be negative.
-
What are some common mistakes to avoid when converting temperatures? A common mistake is forgetting to add 32 after multiplying by 9/5. Another mistake is using the wrong ratio (e.g., reversing 9/5 to 5/9). Always double-check your calculations to ensure accuracy.
Conclusion: Mastering Temperature Conversion
The ability to convert between Celsius and Fahrenheit is a valuable skill applicable in numerous situations. Understanding the conversion formula, its derivation, and its applications allows for accurate temperature measurements and informed decisions across various fields. Whether you’re a student, a professional, or simply someone curious about the world around you, grasping temperature conversion enhances your understanding of the physical world and enables more effective communication and problem-solving. Remember to always double-check your work and utilize the tools available, whether it’s the formula, a conversion table, or an online calculator, to achieve accurate and reliable results. The key is understanding the underlying principles and applying them correctly.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
36 Oz How Many Pounds
Sep 12, 2025
-
How Fast Is 2000 Knots
Sep 12, 2025
-
13 Acres To Square Feet
Sep 12, 2025
-
What Is 25km In Miles
Sep 12, 2025
-
6 Pies Cuantos Metros Son
Sep 12, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 45 Deg C To F . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.