101 5 F To C
timefordiamonds
Sep 17, 2025 · 5 min read
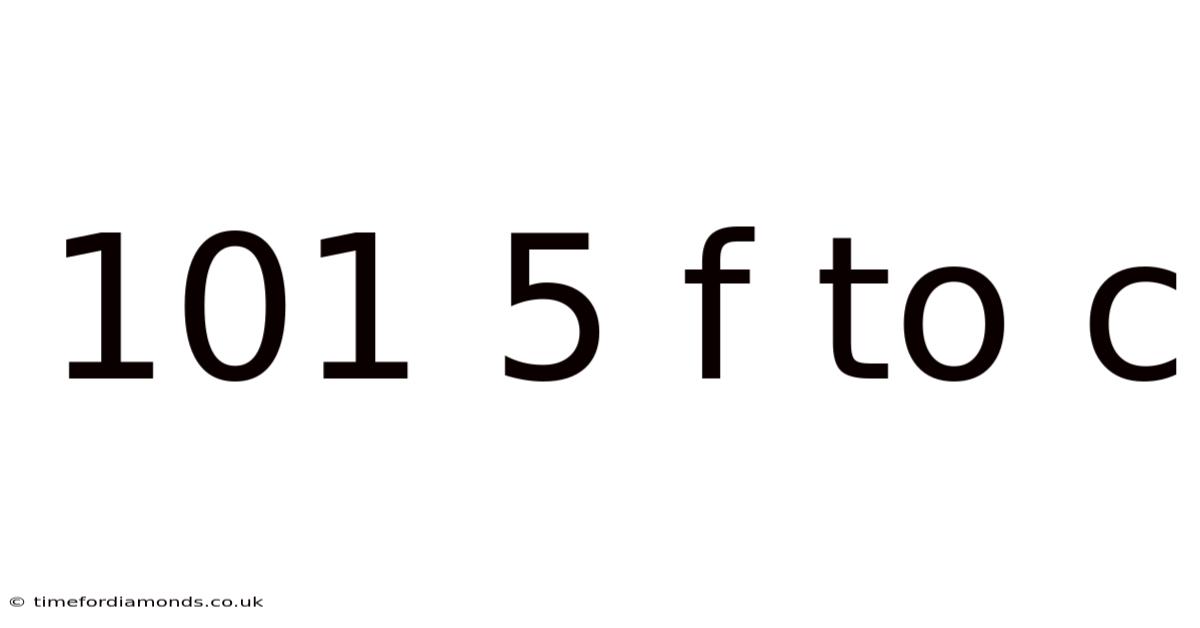
Table of Contents
101 on Converting Fahrenheit to Celsius: A Comprehensive Guide
Converting Fahrenheit (°F) to Celsius (°C) might seem like a simple task, but understanding the underlying principles and mastering the conversion process is crucial for various applications, from everyday life to scientific research. This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about converting Fahrenheit to Celsius, covering the formula, practical examples, the history behind both scales, and frequently asked questions. We'll move beyond simple conversion and delve into the "why" behind the calculations, ensuring a thorough understanding of this fundamental concept.
Understanding the Fahrenheit and Celsius Scales
Before diving into the conversion process, let's briefly explore the history and characteristics of both temperature scales.
-
Fahrenheit (°F): Developed by Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit in the early 18th century, this scale is based on three reference points: the freezing point of a brine solution (0°F), the freezing point of water (32°F), and the average human body temperature (96°F). While widely used in the United States, its less intuitive relationship to water's freezing and boiling points makes it less preferred in scientific contexts.
-
Celsius (°C): Also known as the centigrade scale, Celsius was proposed by Anders Celsius in the 1740s. This scale is defined by the freezing point of water (0°C) and the boiling point of water (100°C) at standard atmospheric pressure. Its logical and easily understandable reference points have made it the preferred scale in most scientific applications and internationally.
The Formula: Converting Fahrenheit to Celsius
The fundamental formula for converting Fahrenheit to Celsius is:
°C = (°F - 32) × 5/9
This formula reflects the linear relationship between the two scales. The subtraction of 32 accounts for the difference in the freezing point of water (0°C vs. 32°F), and the multiplication by 5/9 adjusts for the different scales' sizes. Let's break down why this works:
-
Subtracting 32: This step aligns the zero points of the two scales. By subtracting 32 from the Fahrenheit temperature, we are essentially shifting the Fahrenheit scale so that the freezing point of water becomes 0, just like in Celsius.
-
Multiplying by 5/9: This accounts for the difference in the size of the degree increments. A change of 9°F is equivalent to a change of 5°C. The fraction 5/9 acts as a conversion factor, ensuring the correct scaling between the two systems.
Practical Examples: Converting Fahrenheit to Celsius
Let's illustrate the conversion process with a few examples:
Example 1: Converting 68°F to Celsius
- Substitute the Fahrenheit value: °C = (68 - 32) × 5/9
- Subtract 32: °C = 36 × 5/9
- Multiply by 5/9: °C = 20
Therefore, 68°F is equal to 20°C.
Example 2: Converting 212°F to Celsius (Boiling point of water)
- Substitute the Fahrenheit value: °C = (212 - 32) × 5/9
- Subtract 32: °C = 180 × 5/9
- Multiply by 5/9: °C = 100
Therefore, 212°F is equal to 100°C. This confirms the boiling point of water in both scales.
Example 3: Converting -4°F to Celsius
- Substitute the Fahrenheit value: °C = (-4 - 32) × 5/9
- Subtract 32: °C = -36 × 5/9
- Multiply by 5/9: °C = -20
Therefore, -4°F is equal to -20°C.
Beyond the Formula: Understanding the Relationship
The formula provides a straightforward method for conversion, but understanding the underlying relationship between the scales offers deeper insight. The linear relationship means that for every increase of 9°F, there's a corresponding increase of 5°C. This consistent ratio is essential to the accuracy of the conversion.
Advanced Applications and Considerations
While the formula provides an accurate conversion for most scenarios, there are a few considerations for more complex applications:
-
Significant Figures: When dealing with scientific measurements, pay attention to significant figures. The number of significant figures in your final answer should reflect the precision of your input.
-
Rounding: Rounding appropriately is crucial to avoid introducing errors. Consider the context of the measurement and the required level of accuracy when rounding your final result.
-
Extreme Temperatures: While the formula works across a wide range of temperatures, extremely high or low temperatures might require adjustments for certain materials and physical phenomena.
-
Kelvin Scale: For scientific work, especially in thermodynamics, the Kelvin scale is frequently used. The Kelvin scale is an absolute temperature scale, where 0 Kelvin represents absolute zero (the theoretical absence of all thermal energy). Converting Celsius to Kelvin is simpler: K = °C + 273.15
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Why are there two different temperature scales?
A1: Historically, different scales developed independently, with varying reference points. Fahrenheit gained early adoption in some regions, while Celsius, with its more intuitive water-based reference points, eventually became the international standard for scientific and many other applications.
Q2: Is it always necessary to use the formula?
A2: While the formula provides the most accurate results, for common conversions, you might find online converters or temperature conversion charts helpful. However, understanding the formula remains crucial for solving more complex problems and ensuring accuracy.
Q3: Can I convert Celsius to Fahrenheit?
A3: Yes, the reverse conversion is equally important. The formula for converting Celsius to Fahrenheit is: °F = (°C × 9/5) + 32
Q4: What are some real-world applications of temperature conversion?
A4: Temperature conversion is essential in numerous fields including:
- Cooking: Converting recipes from one system to another.
- Medicine: Monitoring patient temperatures accurately.
- Meteorology: Reporting weather conditions internationally.
- Engineering: Designing and testing equipment for various environments.
- Scientific research: Conducting experiments and reporting results using a standard unit.
Q5: Are there any online tools to help with conversion?
A5: Many websites and applications offer temperature conversion calculators that can perform the conversion for you automatically. However, it’s always beneficial to understand the underlying formula for a comprehensive understanding.
Conclusion
Converting Fahrenheit to Celsius is a fundamental skill with broad applications. While the formula itself might appear simple, mastering it provides a solid understanding of different temperature scales and their interrelationship. By understanding both the practical application of the formula and the reasoning behind it, you are equipped to confidently navigate temperature conversions in various contexts, whether it's adjusting a recipe or analyzing scientific data. Remember that beyond simply plugging numbers into a formula, the true understanding lies in grasping the underlying principles that define the relationship between Fahrenheit and Celsius scales.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
100 000 Millas A Km
Sep 17, 2025
-
Convert Cm To Ml Calculator
Sep 17, 2025
-
Medio Kilo Cuantas Libras Son
Sep 17, 2025
-
How Much Is 1 Km
Sep 17, 2025
-
26 Acres To Square Feet
Sep 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 101 5 F To C . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.