1 Atm To N M2
timefordiamonds
Sep 13, 2025 · 5 min read
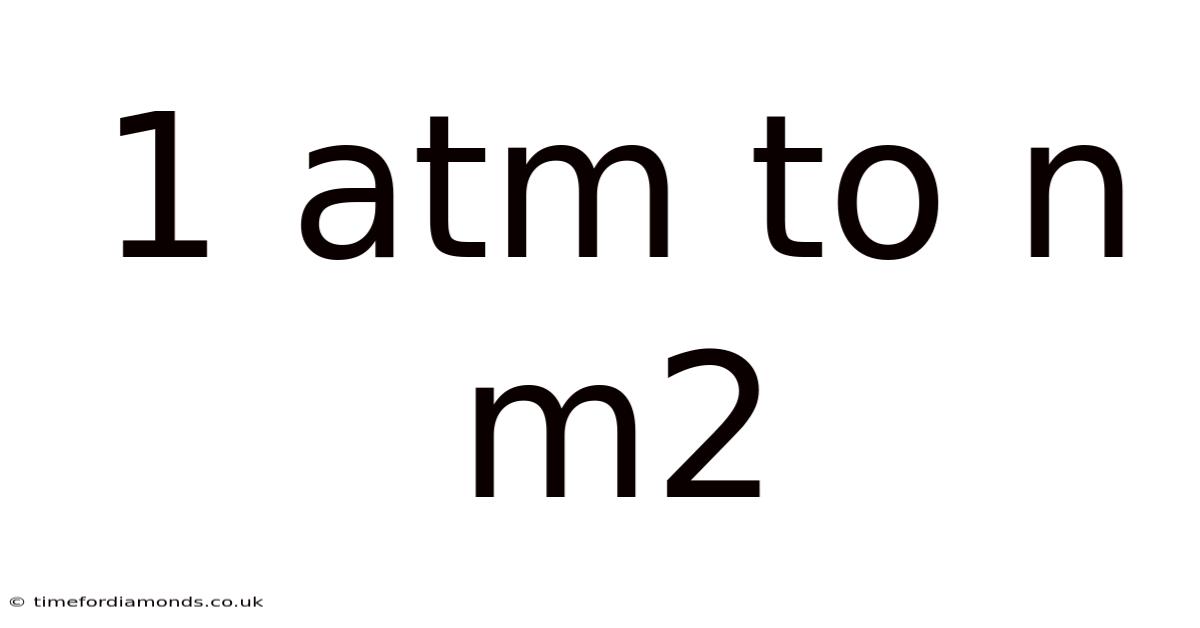
Table of Contents
Understanding the Conversion: 1 ATM to N/m² (Pascals)
The relationship between atmospheric pressure (ATM) and Pascals (N/m²) is fundamental in physics and engineering. Understanding this conversion is crucial for anyone working with pressure measurements, from meteorology and aviation to materials science and fluid dynamics. This article will comprehensively explain how to convert 1 ATM to N/m², exploring the underlying principles and providing practical examples to solidify your understanding. We'll delve into the definition of each unit, explain the conversion factor, and address common misconceptions.
Understanding Atmospheric Pressure (ATM)
Atmospheric pressure is the force exerted by the weight of the air above a given surface area. It's essentially the pressure exerted by the column of air stretching from that point to the top of the atmosphere. This pressure varies with altitude, temperature, and weather conditions. At sea level, under standard atmospheric conditions, the average atmospheric pressure is approximately 1 ATM. It's important to note that ATM isn't a standardized unit in the International System of Units (SI), but rather a unit of convenience often used in everyday life and certain scientific contexts.
Understanding Pascals (N/m²)
The Pascal (Pa), named after the renowned French scientist Blaise Pascal, is the SI unit of pressure. It's defined as one Newton (N) of force acting perpendicularly on a one-square-meter (m²) area. A Newton, in turn, is the SI unit of force, defined as the force required to accelerate a one-kilogram mass at a rate of one meter per second squared (1 kg⋅m/s²). Therefore, a Pascal can be expressed as N/m², representing force per unit area. This is a more fundamental and scientifically precise unit compared to ATM.
The Conversion Factor: From ATM to Pascals
The key to converting 1 ATM to Pascals lies in the established equivalence between these two units. The standard atmospheric pressure (1 ATM) is defined as 101,325 Pascals (Pa) or 101,325 N/m². This value is derived from experimental measurements and serves as the foundation for many pressure calculations.
Therefore, the conversion is straightforward:
1 ATM = 101,325 Pa = 101,325 N/m²
This means that the force exerted by the atmosphere at sea level on a one-square-meter area is approximately 101,325 Newtons.
Step-by-Step Conversion Process
While the conversion itself is simple (multiplying by 101,325), let's outline a step-by-step process for clarity, especially when dealing with pressures other than 1 ATM.
-
Identify the pressure in ATM: Let's say we have a pressure of 'x' ATM.
-
Apply the conversion factor: Multiply the pressure in ATM by the conversion factor: x ATM * 101,325 Pa/ATM.
-
Obtain the pressure in Pascals: The result will be the pressure in Pascals (Pa) or N/m².
Example:
Convert 2.5 ATM to Pascals.
2.5 ATM * 101,325 Pa/ATM = 253,312.5 Pa or 253,312.5 N/m²
The Scientific Basis: Pressure, Force, and Area
The conversion between ATM and Pascals hinges on the fundamental relationship between pressure, force, and area. Pressure is defined as the force applied per unit area. The formula is:
Pressure (P) = Force (F) / Area (A)
This relationship is crucial because it explains why Pascal is expressed as N/m². A larger force acting on the same area results in higher pressure, and the same force acting on a smaller area results in higher pressure.
Practical Applications: Where is this Conversion Used?
The conversion between ATM and Pascals is fundamental in numerous fields:
-
Meteorology: Weather reports often provide atmospheric pressure readings, which are typically converted between ATM and Pascals for accurate scientific analysis and modeling.
-
Aviation: Aircraft design and operation heavily rely on precise pressure measurements for altitude calculations, flight control, and cabin pressurization. The conversion is crucial for ensuring safety and performance.
-
Fluid Mechanics: In studying fluid behavior, understanding pressure differences is essential. Converting between ATM and Pascals allows for consistent and accurate calculations in various fluid dynamics applications.
-
Materials Science: Materials scientists utilize pressure measurements in various experiments and processes, such as studying material behavior under high pressure or analyzing the strength of materials.
-
Engineering: Pressure calculations are vital in engineering disciplines, including designing pressure vessels, pipelines, and other systems that handle pressurized fluids or gases. Accurate conversion between ATM and Pascals is key to ensuring structural integrity and safety.
-
Deep Sea Exploration: Submersibles and other deep-sea equipment operate under immense pressure. Accurate conversion between ATM and Pascals is vital for designing and operating these systems.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Is 1 ATM always equal to 101,325 Pa?
A1: While 101,325 Pa is the standard atmospheric pressure at sea level, it's important to remember that atmospheric pressure varies with altitude and weather conditions. At higher altitudes, atmospheric pressure is lower. The conversion factor remains constant, but the actual value in Pascals will change.
Q2: What other units are used to measure pressure?
A2: Besides ATM and Pascals, many other units are used to measure pressure, including:
- Bar: 1 bar = 100,000 Pa
- Millibar (mbar): 1 mbar = 100 Pa
- Millimeter of Mercury (mmHg) or Torr: Frequently used in medical and scientific applications.
- Inches of Mercury (inHg): Commonly used in some weather reports.
- Pounds per square inch (psi): Widely used in engineering and industrial applications.
Q3: Why is it important to use the correct unit?
A3: Using the correct unit is crucial for accuracy and avoiding errors in calculations and analyses. Incorrect units can lead to significant discrepancies and potentially dangerous consequences in engineering and scientific applications.
Q4: How can I perform conversions between other pressure units?
A4: To convert between other pressure units, you'll need the appropriate conversion factors. These factors can be found in scientific handbooks or online resources. The process typically involves multiplying or dividing the pressure value by the relevant conversion factor.
Conclusion
The conversion of 1 ATM to N/m² (Pascals) is a fundamental calculation in many scientific and engineering disciplines. Understanding this conversion requires grasping the concepts of atmospheric pressure, force, area, and the relationship between them. The conversion factor of 101,325 Pa/ATM simplifies the process, enabling accurate calculations in diverse applications. Remember that while 101,325 Pa represents standard atmospheric pressure at sea level, variations exist due to altitude and weather conditions. Accurate and consistent unit usage is essential for reliable results and avoids potential errors in any pressure-related work. By understanding this fundamental conversion, you'll be better equipped to tackle more complex problems involving pressure measurements and calculations.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
74 Kg How Many Pounds
Sep 13, 2025
-
47 Meters How Many Feet
Sep 13, 2025
-
Feet Per Min To Mph
Sep 13, 2025
-
Cuantos Pies Son 180 Centimetros
Sep 13, 2025
-
Cuantos Minutos Son 25 Millas
Sep 13, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 1 Atm To N M2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.